Airplane traffic in Israel has begun to pick up speed and Israelis are preparing to get some fresh air from the period of hard fighting, boarding flights or planning a vacation for Passover. However, a measles epidemic is raging right now, mainly in ten countries before them, the World Health Organization is now warning.
Spreading here too: the incurable disease that is raging in Europe and the USA
Continues to spread in Israel: everything you need to know about the measles disease
For several months now, the measles epidemic has been spreading mainly throughout Europe, and a high wave of infections has also been reported in Israel: in recent weeks, almost 30 measles patients have been registered, some of whom were infected while visiting one of the infected European countries. The World Health Organization warned last week that millions of people in Europe are at risk due to the spread of the virus.
The three countries at the top of the list are Kazakhstan with over 15 thousand cases of infection during 2023, Azerbaijan where approximately 14 thousand cases were recorded and Russia with almost 13 thousand cases. Measles is also spreading in Kyrgyzstan where 7,044 cases were reported, Turkey with 4,559 cases of infection, Romania where 1,753 cases were reported, Uzbekistan – 1,107 cases. In eighth place is Armenia with 554 cases of infection, followed by Tajikistan with 294 cases and the United Kingdom closes the list with a high number of 231 cases of infection.
The Ministry of Health called on the public to make sure that children and adults are vaccinated: babies must receive two vaccinations from the age of one, with an interval of one month between them. Those born before 1957 and exposed to the virus in childhood do not need to be vaccinated. Children up to the age of 6 who are not vaccinated need the vaccines in the drops of milk, children over the age of 7 need to complete vaccinations through the health services for students and adults in the health insurance funds. The Ministry of Health recommends that pregnant women who are not vaccinated with two doses and people suffering from immunosuppression who have been exposed to one of the patients – contact their family doctor or emergency medicine centers to receive a preventive vaccine.
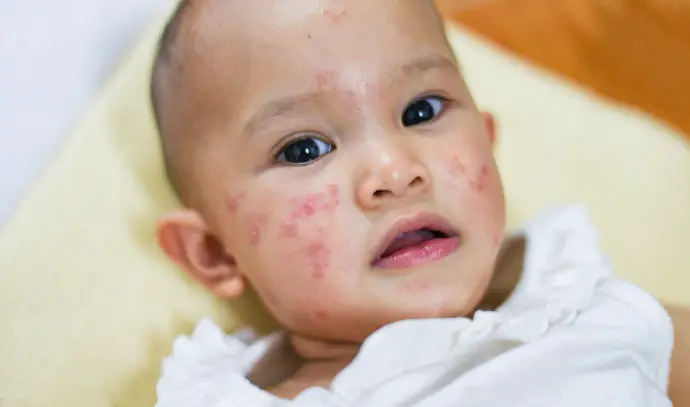
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease that manifests itself in fever, general malaise, runny nose and rash and may have severe and even life-threatening complications years after infection. The Ministry of Health stressed to patients who need to go to the clinic or the emergency room, that they must coordinate their arrival and notify the medical staff upon arrival, so that they will be placed in an isolated room away from crowds. If symptoms appear, until a medical examination, stay in public spaces such as shopping malls, public transport, work and studies should be avoided.
Questions and Answers
Why did the measles panic begin?
Since last December, almost 30 people in Israel have been diagnosed with the viral disease, which is spreading at record speed. As mentioned, tens of thousands of infected people have been found in recent months in Europe as well. This is a viral disease that most times is not dangerous, but in rare cases can cause severe brain damage and even death. The only way to protect against it is through vaccination, since there is no antibiotic treatment that cures the disease.
What causes the disease?
The cause of measles is the morbillivirus. Humans are the only hosts of this virus.
How do you get the disease?
The virus spreads through contact with saliva fragments or nasal, oral or throat fluids from an infected person. Sneezes, coughs, kisses and runny noses can infect those around them who are not vaccinated. Fragments of the virus enter the body through the respiratory system or through contact with the eyes.
How and when do you get vaccinated?
The measles vaccine is given in two doses at least four weeks apart.
Who needs to be vaccinated and who is exempt?
Those born before 1957 are considered naturally vaccinated and therefore do not need to be vaccinated. In those years, the vaccine was not given in the world. Those born in 1957-1966 are considered unvaccinated even though most of them were naturally vaccinated. The Ministry of Health recommends vaccination only if there was exposure to measles. In those years, vaccination was given worldwide, but not in Israel. Those born between 1967-1977 are considered 95% vaccinated. The Ministry of Health recommends getting vaccinated with one dose – only if there was exposure to measles. In those years, one vaccine dose was given in Israel. Those born in 1978 and later were given two doses of the measles vaccine, so residents are considered vaccinated. The Ministry of Health states that when there is exposure to measles, one must check if the person is vaccinated according to the vaccination routine and supplement them as needed. In addition, the Ministry of Health urges anyone who fears being around a measles patient and is not vaccinated with two doses, to contact the Voice of Health center at Kochavit 5400.
Where can I get vaccinated?
Babies and children receive the vaccine as part of a drop of milk. Teenagers and adults can get vaccinated at the traveling clinics in the hospitals throughout the country and at the district health bureaus of the Ministry of Health. More details can also be obtained at the health center of the Ministry of Health.
What are the symptoms of measles?
Measles is a serious infectious disease manifested by cough, runny nose, high fever, rash characteristic of the disease and lesions in the oral cavity and conjunctivitis. After an incubation period, which lasts eight to 12 days from the moment of infection and during which the virus spreads in the body, the first stage (prodrome) begins, which causes fever, eye inflammation, fear of light (photophobia), runny nose and cough. In 50-70 percent of patients, red-blue lesions will appear on the inside of the cheeks and in the mouth. These are lesions unique to the disease, called "Koplick's points". These lesions may spread to the lips, gums, palate, eyelids and vagina. The rash starts around the forehead, near the hairline, behind the ears and on the neck and spreads down to the chest, abdomen and legs – up to the ankles. Within about a week the rash recedes, but the cough may last up to ten days. In severe cases, enlarged lymph nodes appear.
What are the risks of the disease?
Children under the age of 5 or adults over the age of 20 may be in danger if they become infected and become ill. The main cause of death from the disease is pneumonia, which is caused by bacteria that attack the lungs and cause a secondary infection. Common such bacteria are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus – all of which cause severe and life-threatening pneumonia.
The disease makes the body more sensitive to many other infections, including inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media), inflammation of the mastoid bone, located behind the ear and close to the meninges (mastoiditis), inflammation of the appendix (appendicitis), inflammation of the myocardium, diarrhea and vomiting until dehydration and other infections. The deadliest danger of all is a complication of measles called SSPE – a chronic systemic encephalitis that almost always ends in death. This inflammation breaks out between seven and 13 years from the moment of infection, after the virus becomes particularly violent in an unknown way, causing the destruction of brain cells and death in all patients.
I don't remember if I was vaccinated before. How can you check it?
The family doctor will send you for a blood test to measure antibodies against the virus called Measles Ab and if the antibody level is high enough, no further vaccination is needed now.
How long does the measles vaccine last?
Protection from the measles vaccine after receiving the required two doses continues in over 96% of those vaccinated – for decades.
Is there a cure for measles?
Today there is no cure for measles. Antibiotics only work against bacteria, so they do not affect the measles virus at all. Antiviral treatments (such as those used for herpes or AIDS) have been found to be ineffective. The only treatment is supportive: fluid infusion and treatment of the complications of the disease. Hence the main importance in preventing the serious disease.